nf-core/genomicrelatedness
Bioinformatics pipeline for estimating genetic relatedness from low-coverage whole-genome sequencing (sWGS) data
Introduction
nf-core/genomicrelatedness is a bioinformatics pipeline that for estimating genetic relatedness from low-coverage whole-genome sequencing (sWGS) data. It performs read mapping, optional base quality score recalibration, variant calling with GATK and BCFtools, and downstream relatedness estimation using multiple complementary tools. For many non-model organisms, no high-confidence variant set is available. The pipeline provides an automated multi-round bootstrapping workflow to generate one. The resulting standardized outputs include genotype likelihood-based variant calls, filtered VCF files, and relatedness estimates from several independent algorithms, enabling robust inference even from very sparse sequencing data.
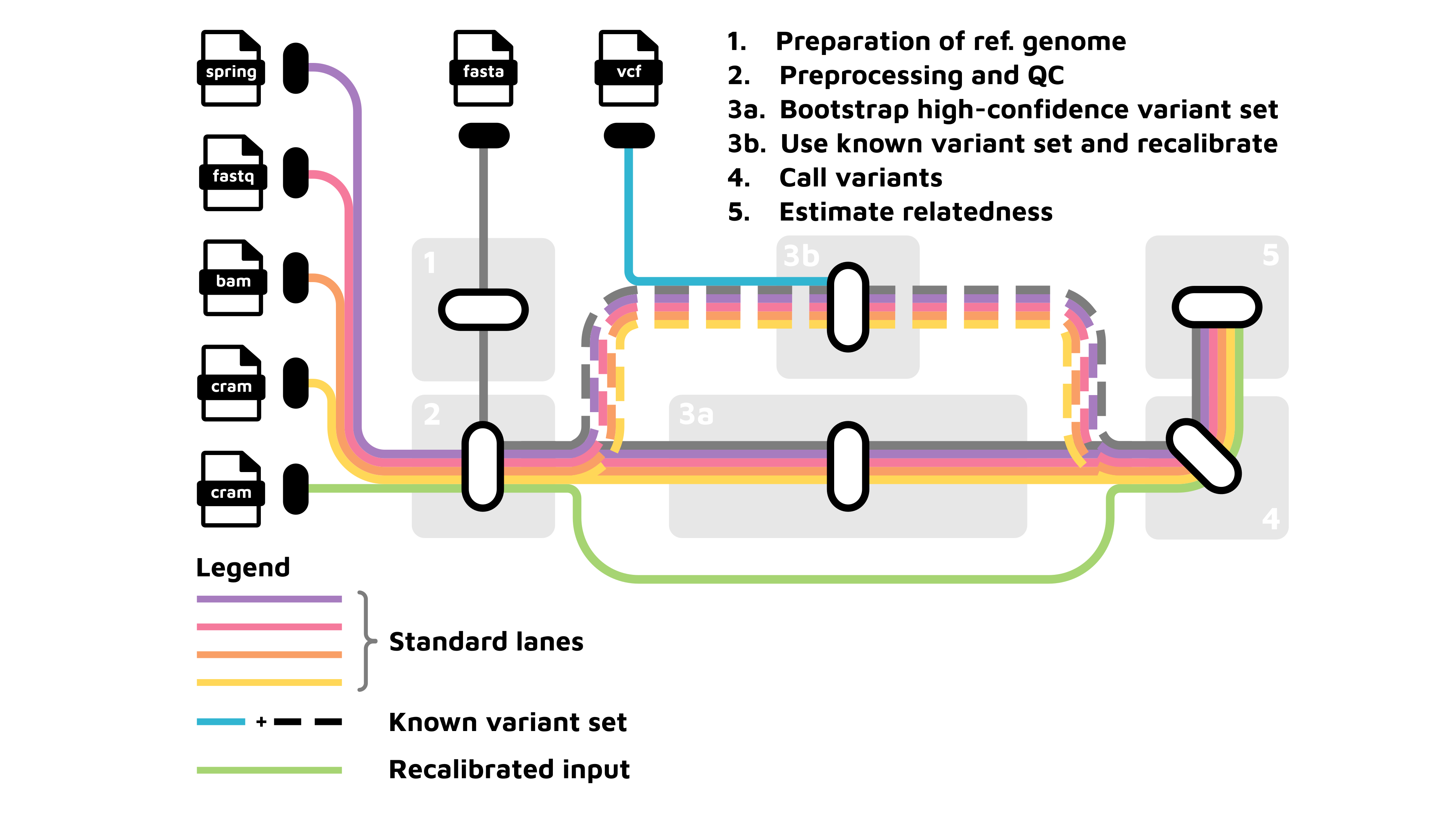
The pipeline can perform the following major processing stages:
-
Input parsing & metadata setup: Reads a CSV samplesheet describing the input FASTQ, SPRING or CRAM files and their read-group information.
-
Reference genome preparation: If not provieded, this step automatically generates:
- BWA-MEM2 index files
- FASTA index (.fai)
- Sequence dictionary (.dict)
- Read alignment
- Aligns raw FASTQ reads to the reference genome.
- Produces sorted, indexed CRAM files with proper read-group annotations.
-
If a known variant set is provided, runs Base Quality Score Recalibration.
-
If no known variant set is available, the pipeline can generate one automatically via bootstrapping.
- Iteratively refines and stabilises the set of high-confidence SNPs for downstream use.
-
Runs Base Quality Score Recalibration if a known variant set was provided.
-
Variant calling (GATK HaplotypeCaller & BCFtools)
-
Performs joint variant discovery for all samples.
-
Combines GATK and BCFtools results using bcftools isec to produce a conservative, high-confidence set of variants.
-
Variant filtering & thinning and optional exclusion of specific scaffolds.
-
Relatedness estimation (multi-tool) Uses multiple complementary tools to increase robustness, depending on configuration:
- READv2 (ML-based relatedness estimation for low-coverage data)
- BREADR (R-based Bayesian relatedness inference)
- NGSrelate/ANGSD (likelihood-based estimation directly from genotype likelihoods)
- MultiQC reporting: Aggregates quality metrics across all workflow stages into a single interactive report.
Usage
If you are new to Nextflow and nf-core, please refer to this page on how to set-up Nextflow. Make sure to test your setup with -profile test before running the workflow on actual data.
First, prepare a samplesheet with your input data that looks as follows:
samplesheet.csv:
sample,fastq_1,fastq_2
CONTROL_REP1,AEG588A1_S1_L002_R1_001.fastq.gz,AEG588A1_S1_L002_R2_001.fastq.gz
CONTROL_REP1,AEG588A1_S1_L003_R1_001.fastq.gz,AEG588A1_S1_L003_R2_001.fastq.gz
CONTROL_REP1,AEG588A1_S1_L004_R1_001.fastq.gz,AEG588A1_S1_L004_R2_001.fastq.gz
Each row represents a fastq file (single-end) or a pair of fastq files (paired end). Alternatively, the samplesheet can be filled with fastq files encoded in SPRING format, or the preprocessing steps can be skipped entirely when BAM or CRAM files are provided.
Now, you can run the pipeline using:
nextflow run nf-core/genomicrelatedness \
-profile <docker/singularity/.../institute> \
--input samplesheet.csv \
--fasta <REFGENOME>
--bootstrapping_rounds 1\
--outdir <OUTDIR>Note: If the parameter
--bootstrapping_roundsis provided, it must be an integer between 0 and 3, with 0 having no effect.
Please provide pipeline parameters via the CLI or Nextflow -params-file option. Custom config files including those provided by the -c Nextflow option can be used to provide any configuration except for parameters; see docs.
For more details and further functionality, please refer to the usage documentation and the parameter documentation.
Pipeline output
To see the results of an example test run with a full size dataset refer to the results tab on the nf-core website pipeline page. For more details about the output files and reports, please refer to the output documentation.
Credits
nf-core/genomicrelatedness was originally written by Thomas Isensee. This work was carried out as part of the bwRSE4HPC initiative, funded by the Baden-Württemberg Ministry of Science, Research and Arts, coordinated by the Scientific Software Center (SSC) at Heidelberg University and the Scientific Computing Center (SCC) at KIT.
We thank the following people for their extensive assistance in the development of this pipeline:
- Gisela H. Kopp
- Till Dorendorf
Contributions and Support
If you would like to contribute to this pipeline, please see the contributing guidelines.
For further information or help, don’t hesitate to get in touch on the Slack #genomicrelatedness channel (you can join with this invite).
Citations
An extensive list of references for the tools used by the pipeline can be found in the CITATIONS.md file.
You can cite the nf-core publication as follows:
The nf-core framework for community-curated bioinformatics pipelines.
Philip Ewels, Alexander Peltzer, Sven Fillinger, Harshil Patel, Johannes Alneberg, Andreas Wilm, Maxime Ulysse Garcia, Paolo Di Tommaso & Sven Nahnsen.
Nat Biotechnol. 2020 Feb 13. doi: 10.1038/s41587-020-0439-x.