22.10.6.
Learn more.
Introduction
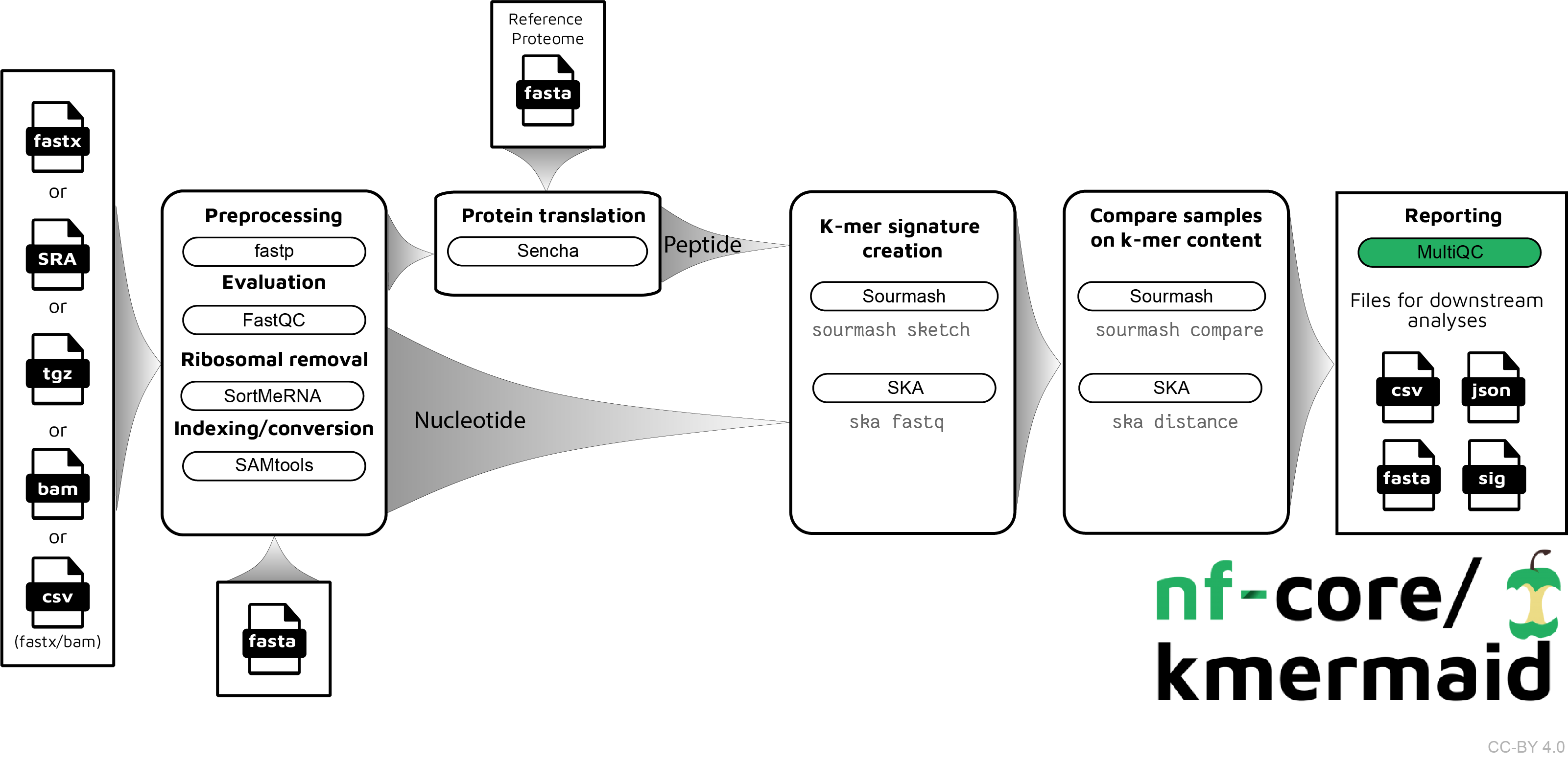
The pipeline is built using Nextflow, a workflow tool to run tasks across multiple compute infrastructures in a very portable manner. It comes with docker containers making installation trivial and results highly reproducible.
Quick Start
i. Install nextflow
ii. Install either Docker or Singularity for full pipeline reproducibility (please only use Conda as a last resort; see docs)
iii. Download the pipeline and test it on a minimal dataset with a single command
nextflow run nf-core/kmermaid -profile test,<docker/singularity/conda/institute>Please check nf-core/configs to see if a custom config file to run nf-core pipelines already exists for your Institute. If so, you can simply use
-profile <institute>in your command. This will enable eitherdockerorsingularityand set the appropriate execution settings for your local compute environment.
iv. Start running your own analysis!
nextflow run nf-core/kmermaid -profile <docker/singularity/conda/institute> --reads '*_R{1,2}.fastq.gz' --genome GRCh37See usage docs for all of the available options when running the pipeline.
Documentation
The nf-core/kmermaid pipeline comes with documentation about the pipeline, found in the docs/ directory:
- Installation
- Pipeline configuration
- Running the pipeline
- Output and how to interpret the results
- Troubleshooting
Usage
With a samples.csv file
nextflow run nf-core/kmermaid --outdir s3://olgabot-maca/nf-kmer-similarity/ --samples samples.csvWith R1, R2 read pairs
nextflow run nf-core/kmermaid --outdir s3://olgabot-maca/nf-kmer-similarity/ \
--read_pairs 's3://olgabot-maca/sra/homo_sapiens/smartseq2_quartzseq/*{R1,R2}*.fastq.gz,s3://olgabot-maca/sra/danio_rerio/smart-seq/whole_kidney_marrow_prjna393431/*{1,2}.fastq.gz'With SRA ids
nextflow run nf-core/kmermaid --outdir s3://olgabot-maca/nf-kmer-similarity/ --sra SRP016501With fasta files
nextflow run nf-core/kmermaid --outdir s3://olgabot-maca/nf-kmer-similarity/ \
--fastas '*.fasta'With bam file
nextflow run czbiohub/nf-kmer-similarity --outdir s3://olgabot-maca/nf-kmer-similarity/ \
--bam 'possorted_genome_bam.bam'With split kmer
nextflow run czbiohub/nf-kmer-similarity --outdir s3://olgabot-maca/nf-kmer-similarity/ --samples samples.csv --split_kmer --subsample 1000Credits
nf-core/kmermaid was originally written by Olga Botvinnik.
Contributions and Support
If you would like to contribute to this pipeline, please see the contributing guidelines.
For further information or help, don’t hesitate to get in touch on Slack (you can join with this invite).
Citation
You can cite the nf-core publication as follows:
The nf-core framework for community-curated bioinformatics pipelines.
Philip Ewels, Alexander Peltzer, Sven Fillinger, Harshil Patel, Johannes Alneberg, Andreas Wilm, Maxime Ulysse Garcia, Paolo Di Tommaso & Sven Nahnsen.
Nat Biotechnol. 2020 Feb 13. doi: 10.1038/s41587-020-0439-x.
ReadCube: Full Access Link