nf-core/mag
Assembly and binning of metagenomes
2.1.0). The latest
stable release is
5.3.0
.
Introduction
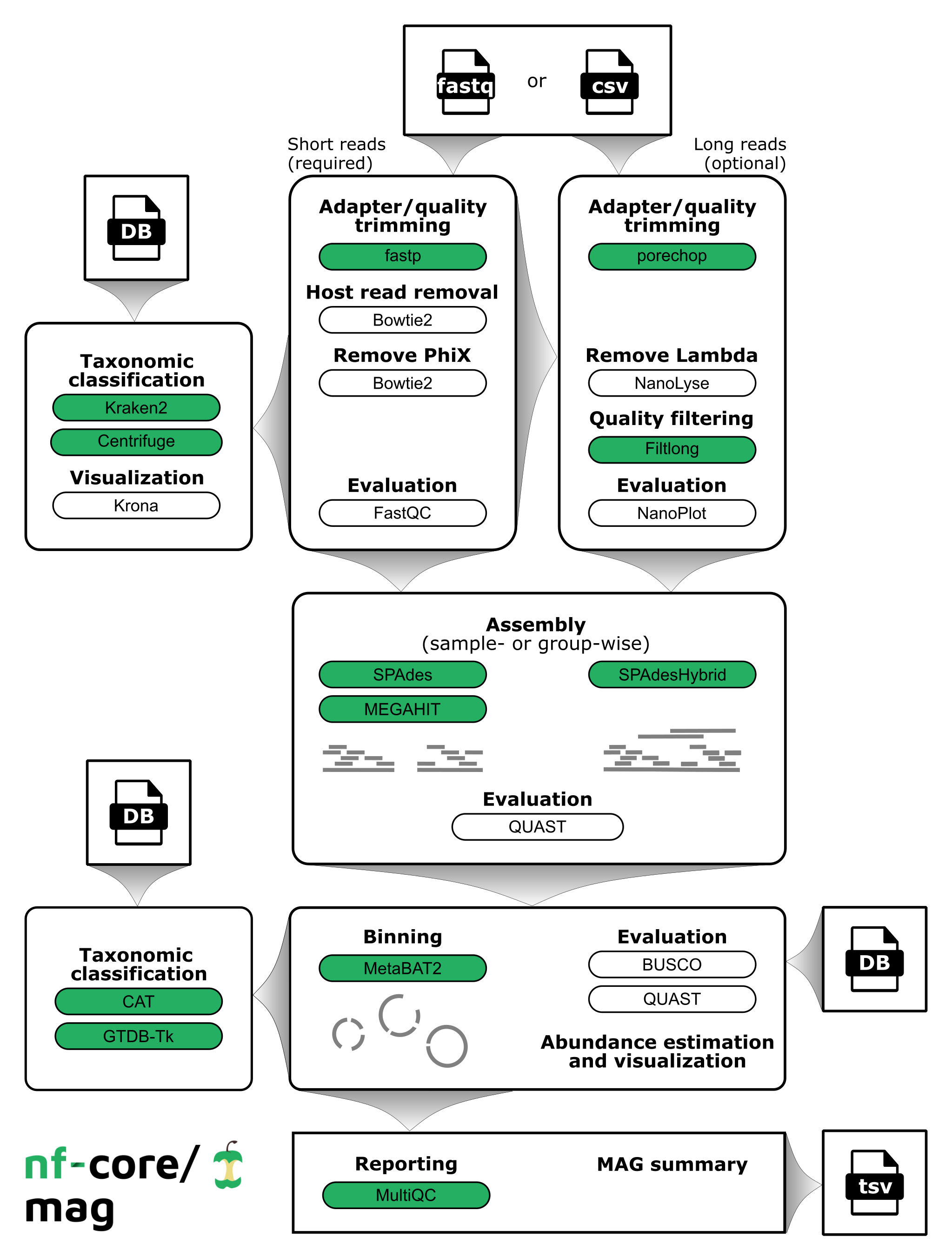
nf-core/mag is a bioinformatics best-practise analysis pipeline for assembly, binning and annotation of metagenomes.
The pipeline is built using Nextflow, a workflow tool to run tasks across multiple compute infrastructures in a very portable manner. It uses Docker/Singularity containers making installation trivial and results highly reproducible. The Nextflow DSL2 implementation of this pipeline uses one container per process which makes it much easier to maintain and update software dependencies. Where possible, these processes have been submitted to and installed from nf-core/modules in order to make them available to all nf-core pipelines, and to everyone within the Nextflow community!
On release, automated continuous integration tests run the pipeline on a full-sized dataset on the AWS cloud infrastructure. This ensures that the pipeline runs on AWS, has sensible resource allocation defaults set to run on real-world datasets, and permits the persistent storage of results to benchmark between pipeline releases and other analysis sources. The results obtained from the full-sized test can be viewed on the nf-core website.
Pipeline summary
By default, the pipeline currently performs the following: it supports both short and long reads, quality trims the reads and adapters with fastp and Porechop, and performs basic QC with FastQC. The pipeline then:
- assigns taxonomy to reads using Centrifuge and/or Kraken2
- performs assembly using MEGAHIT and SPAdes, and checks their quality using Quast
- performs metagenome binning using MetaBAT2, and checks the quality of the genome bins using Busco
- assigns taxonomy to bins using GTDB-Tk and/or CAT
Furthermore, the pipeline creates various reports in the results directory specified, including a MultiQC report summarizing some of the findings and software versions.
Quick Start
-
Install
Nextflow(>=21.04.0) -
Install any of
Docker,Singularity,Podman,ShifterorCharliecloudfor full pipeline reproducibility (please only useCondaas a last resort; see docs) -
Download the pipeline and test it on a minimal dataset with a single command:
nextflow run nf-core/mag -profile test,<docker/singularity/podman/shifter/charliecloud/conda/institute>- Please check nf-core/configs to see if a custom config file to run nf-core pipelines already exists for your Institute. If so, you can simply use
-profile <institute>in your command. This will enable eitherdockerorsingularityand set the appropriate execution settings for your local compute environment. - If you are using
singularitythen the pipeline will auto-detect this and attempt to download the Singularity images directly as opposed to performing a conversion from Docker images. If you are persistently observing issues downloading Singularity images directly due to timeout or network issues then please use the--singularity_pull_docker_containerparameter to pull and convert the Docker image instead. Alternatively, it is highly recommended to use thenf-core downloadcommand to pre-download all of the required containers before running the pipeline and to set theNXF_SINGULARITY_CACHEDIRorsingularity.cacheDirNextflow options to be able to store and re-use the images from a central location for future pipeline runs. - If you are using
conda, it is highly recommended to use theNXF_CONDA_CACHEDIRorconda.cacheDirsettings to store the environments in a central location for future pipeline runs.
- Please check nf-core/configs to see if a custom config file to run nf-core pipelines already exists for your Institute. If so, you can simply use
-
Start running your own analysis!
nextflow run nf-core/mag -profile <docker/singularity/podman/shifter/charliecloud/conda/institute> --input '*_R{1,2}.fastq.gz'or
nextflow run nf-core/mag -profile <docker/singularity/podman/shifter/charliecloud/conda/institute> --input samplesheet.csv
See usage docs and parameter docs for all of the available options when running the pipeline.
Documentation
The nf-core/mag pipeline comes with documentation about the pipeline usage, parameters and output. Detailed information about how to specify the input can be found under input specifications.
Group-wise co-assembly and co-abundance computation
Each sample has an associated group ID (see input specifications). This group information can be used for group-wise co-assembly with MEGAHIT or SPAdes and/or to compute co-abundances for the binning step with MetaBAT2. By default, group-wise co-assembly is disabled, while the computation of group-wise co-abundances is enabled. For more information about how this group information can be used see the documentation for the parameters --coassemble_group and --binning_map_mode.
When group-wise co-assembly is enabled, SPAdes is run on accordingly pooled read files, since metaSPAdes does not yet allow the input of multiple samples or libraries. In contrast, MEGAHIT is run for each group while supplying lists of the individual readfiles.
Credits
nf-core/mag was written by Hadrien Gourlé at SLU, Daniel Straub and Sabrina Krakau at the Quantitative Biology Center (QBiC).
Long read processing was inspired by caspargross/HybridAssembly written by Caspar Gross @caspargross
We thank the following people for their extensive assistance in the development of this pipeline:
- Alexander Peltzer
- Phil Ewels
- Gisela Gabernet
- Harshil Patel
- Johannes Alneberg
- Maxime Borry
- Maxime Garcia
- Michael L Heuer
Contributions and Support
If you would like to contribute to this pipeline, please see the contributing guidelines.
For further information or help, don’t hesitate to get in touch on the Slack #mag channel (you can join with this invite).
Citations
If you use nf-core/mag for your analysis, please cite it using the following doi: 10.5281/zenodo.3589527
An extensive list of references for the tools used by the pipeline can be found in the CITATIONS.md file.
You can cite the nf-core publication as follows:
The nf-core framework for community-curated bioinformatics pipelines.
Philip Ewels, Alexander Peltzer, Sven Fillinger, Harshil Patel, Johannes Alneberg, Andreas Wilm, Maxime Ulysse Garcia, Paolo Di Tommaso & Sven Nahnsen.
Nat Biotechnol. 2020 Feb 13. doi: 10.1038/s41587-020-0439-x.